Definitions
05.02.14 / Definitions / Author: admin / Comments: (6)
Biopsy – This is the removal of a sample of tissue from the body to test and diagnose for disease. Also called a Breast Core Biopsy.
DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ) – abnormal cells changes that are contained within the milk ducts of the breast. Sometimes called pre-cancer or pre-invasive cancer.
Further information here: http://canceraustralia.gov.au/affected-cancer/cancer-types/breast-cancer/about-breast-cancer/types-breast-cancer/what-ductal-carcinoma-situ-dcis
DITI (Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging) – is a modern completely safe, radiation free medical technology that involves no contact, compression or discomfort.
It records your skin surface temperatures which can reflect the health of your body.
Infrared technology can detect abnormal infrared patterns in soft tissues including nerves, muscles, tendons, ligaments and organs (physiology). It can show areas of inflammation, infection, injury, nerve irritation/under activity.
Fibroadenoma – is a tumour in the breast, usually benign, made up of mixed fibrous and glandular tissue.
Further information here: http://www.thewomens.org.au/uploads/downloads/HealthInformation/FactSheets/English/BreastCare/fibroadenomas_English.pdf
FNA (Fine Needle Aspiration) – procedures used to investigate superficial lumps or masses. A thin, hollow needle is used to take a sample of cells from an organ or lump under the skin. If the lump can’t be felt under the skin (ie it isn’t palpable), an ultrasound may be used for guidance. The sample is then sent to pathology for examination.
IDC (Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma) – abnormal cells changes in the milk ducts of the breast. Invasive means the abnormal cells have spread out of the duct and into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of Breast Cancer.
Mammogram – Low dose Xray used for screening and diagnosis of breast tissue.
Further information here: www.breastscreen.org.au, www.cancer.org.au, www.bcna.org.au/living-breast-cancer/follow-care/breast-imaging
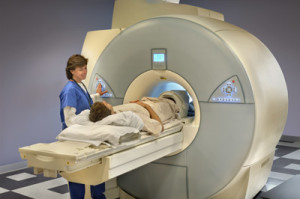
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)– allows viewing of the soft tissues of the body. It is painless and does not use Xrays. It uses a very large magnet and very low-energy radio waves. Diseased tissue gives off a different signal from healthy tissue, which the MRI detects.
A standard MRI for breasts takes approximately 30 minutes. You will usually be lying face down. A contrast dye is sometimes also injected to allow greater visibility of the tissue.
Radiographer – medical imaging technologist who performs medical imaging using and producing high quality Xrays used to diagnose and treat injury or disease.
Radiologist – specialist medical doctor with postgraduate training in performing and interpreting diagnostic imaging tests and procedures (i.e Xray, ultrasound and MRI).
Ultrasound (also called a Sonogram)– Uses high frequency soundwaves to study internal structures of the body. The reflected sounds or echoes create and image for the Radiologist to read and interpret. Ultrasounds are mainly non-invasive (except for pelvic or obstetric examinations).